A Simulationist's Framework
for Business Analysis
Part 03:
What Is Business Analysis?
R.P. Churchill
CBAP, PMP, CSPO, CSM, CSDLean Six Sigma Black Belt
www.rpchurchill.com/presentations/TWSLseries/03_WhatIsBA www.rpchurchill.com | Portfolio | Presentations
30 Years of Simulation
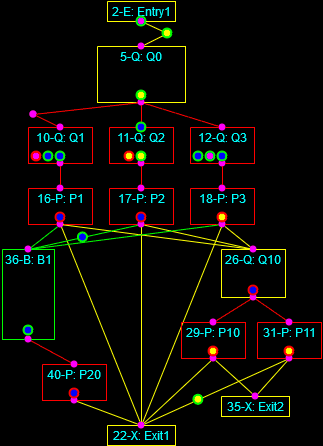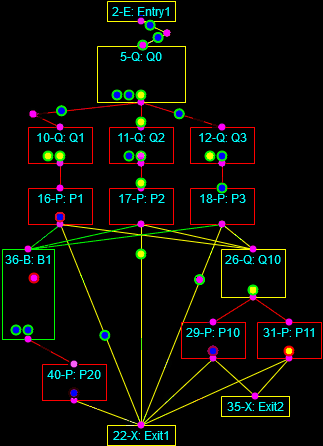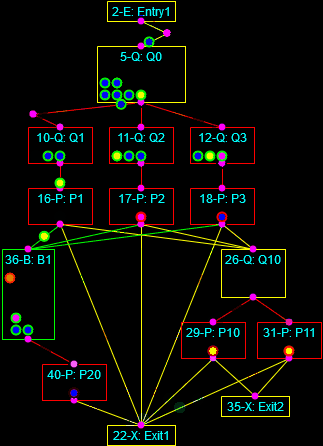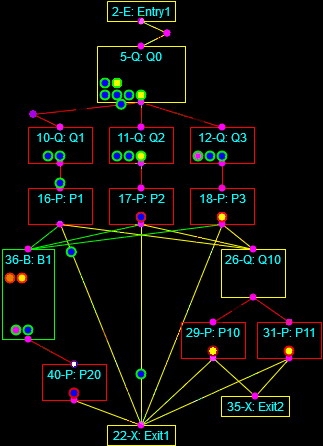
Continuous simulation of the heating of a square billet and Discrete-Event simulation of a multi-phase process.
30 Years of Simulation
|
Industries
|
|
|
BABOK Definition
"Business analysis is the practice of enabling change in an enterprise by defining needs and recommending solutions that deliver value to stakeholders. Business analysis enables an enterprise to articulate needs and the rationale for change, and to design and describe solutions that deliver value."
The practice is difficult to get a mental grip on because it can be rather nebulous and yet all-encompassing. Like my favorite partner dance, which I referred to last week, I can't always tell when you are doing it, but I can surely tell you when you're not doing it.
It can involve strategy, tactics, or operations. It can be performed in the context of a project or across the environment of an entire organization.
It is about understanding where you are, where you're going, and how to get there. (This is almost the biggest thing you need to understand.)
Business Analysis Perspectives
- Agile: How to get people to work together to effect useful change in an efficient manner. (It's all about communication!)
- Business Intelligence: It's all about the data! (A future talk will address this.)
- Information Technology: IT systems aren't the only reason to do this work, but it often seems like it.
- Business Architecture: How to manage, shape, and inspire the organization.
- Business Process Management: (Physical and information) stuff comes in, gets worked on, and goes out. (See SIPOC and COPIS.)
Business Analysis Roles and Interfaces
|
Roles Served In
|
|
Roles Worked With
|
One doesn't tend to start a career in one of the roles on the left. Rather, one tends to grow into them from the more specialized roles on the right.
My Framework:
- Project Planning
- Intended Use
- Assumptions, Capabilities, Limitations, and Risks and Impacts
- Conceptual Model (As-Is State)
- Data Sources, Collection, and Conditioning
- Requirements (To-Be State: Abstract)
- Functional (What it Does)
- Non-Functional (What it Is, plus Maintenance and Governance)
- Design (To-Be State: Detailed)
- Implementation
- Test
- Operation, Usability, and Outputs (Verification)
- Outputs and Fitness for Purpose (Validation)
- Acceptance (Accreditation)
- Project Close
My Basic Framework: Simplified
 Intended Use
Intended Use Conceptual Model (As-Is State)
Conceptual Model (As-Is State) Data Sources, Collection, and Conditioning
Data Sources, Collection, and Conditioning Requirements (To-Be State: Abstract)
Requirements (To-Be State: Abstract)- Functional (What it Does)
- Non-Functional (What it Is, plus Maintenance and Governance)
 Design (To-Be State: Detailed)
Design (To-Be State: Detailed) Implementation
Implementation Test
Test- Operation, Usability, and Outputs (Verification)
- Outputs and Fitness for Purpose (Validation)
My Basic Framework: Iteration and Communication
Regardless of the structure of the engagement, the activities in each phase are carried out in an iterative fashion that continuously incorporates review, feedback, and correction both within and between phases.

Link to detailed discussion.
Structure of the BABOK
Chapter 1: Introduction (structure of the BABOK)
Chapter 2: Key Concepts (basic context of business analysis)
Chapters 3-8: Knowledge Areas (the basic flow of what gets done)
Chapter 9: Underlying Competencies (Analysis, Behavior, Domain Knowledge, Communication, Interaction, Tools/Tech)
Chapter 10: Techniques (50)
Chapter 11: Perspectives (Agile, BI, IT, Business Architecture, Process Management)
Appendices
BABOK Knowledge Areas vs. Bob's Framework
| Bob's Framework | Business Analysis Planning and Monitoring | Elicitation and Collaboration | Requirements Life Cycle Management | Strategy Analysis | Requirements Analysis and Design Definition | Solution Evaluation | Requirements per BABOK |
| Project Planning | X | x | |||||
| Intended Use | x | X | x | x | x | Business Requirements | |
| Assumptions, Capabilities, Limitations, and Risks & Impacts | x | X | x | ||||
| Conceptual Model (As-Is State) |
x | X | X | ||||
| Data Sources, Collection, and Conditioning | x | X | |||||
| Requirements (To-Be State: Abstract) |
x | X | X | x | X | Stakeholder Requirements | |
| Design (To-Be State: Concrete) |
x | x | X | X | Solution Requirements (Functional and Non-Functional) |
||
| Implementation | x | X | x | X | x | x | Transition Requirements |
| Test Operation, Usability, and Outputs (Verification) |
x | X | |||||
| Test Outputs and Fitness for Purpose (Validation) |
x | x | X | ||||
| Acceptance (Accreditation) |
x | X |
Unified Theory of Business Analysis
- Solution vs. Engagement
- Fifty Business Analysis Techniques
- Commonly Used Software Tools
- Management Contexts
- Business Analysis within Project Management
Link to detailed discussion.
Unified Theory 1: The Solution vs. The Engagement

|

|
How much of either process are you a part of?
Link to detailed discussion.
Unified Theory 2: The 50 Techniques
|
|
|
Link to detailed discussion.
Unified Theory 3: Software Tools
| 24 | Excel | Both |
| 14 | Jira | Engagement |
| 14 | Visio | Solution |
| 13 | Word | Both |
| 8 | Confluence | Both |
| 7 | Outlook | Engagement |
| 6 | SharePoint | Engagement |
| 5 | Azure DevOps | Solution |
| 4 | Team Foundation Server | Engagement |
| 4 | PowerPoint | Engagement |
| 3 | Engagement | |
| 3 | Google Docs | Engagement |
| 2 | MS Dynamics | Engagement |
| 2 | Visual Studio | Solution |
| 2 | Notepad | Both |
| 2 | OneNote | Engagement |
| 2 | SQL Server | Solution |
Software greatly aids sharing and communications, so BAs will concentrate on this. However, a huge amount of solutioning will be aided by specific, technical software or will be software, with which BAs may tend to be less involved.
Link to detailed discussion. Link to survey results.
Unified Theory 4: Basic Engagement Contexts



Link to detailed discussion.
Unified Theory 4: Engagement Context Variations



Link to detailed discussion.
Unified Theory 5: Business Analysis Embedded Within Project Management
Project management creates the environment and manages the resources. Business analysis solves the problem.
PMs and BAs are sometimes called "frenemies" There can be plenty of overlap. Do what works!
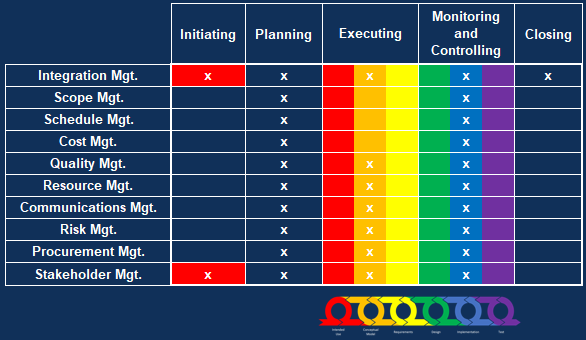
Link to detailed discussion.
Solution Contexts
- internal vs. external customers
- standard solution vs. open-ended solution
- imposed by competition
- opportunity from new technology
- automation
- standardization / modularization
- rearrangement or streamlining
- Lean vs. Six Sigma
- profiling
- incremental vs. The Big Kill
- end-of-life, replacement, and repurposing
- entirely new solutions
- improved management techniques
- general technical solutions
Link to detailed discussion.
This presentation and other information can be found at my website:
E-mail: bob@rpchurchill.com
LinkedIn: linkedin.com/in/robertpchurchill